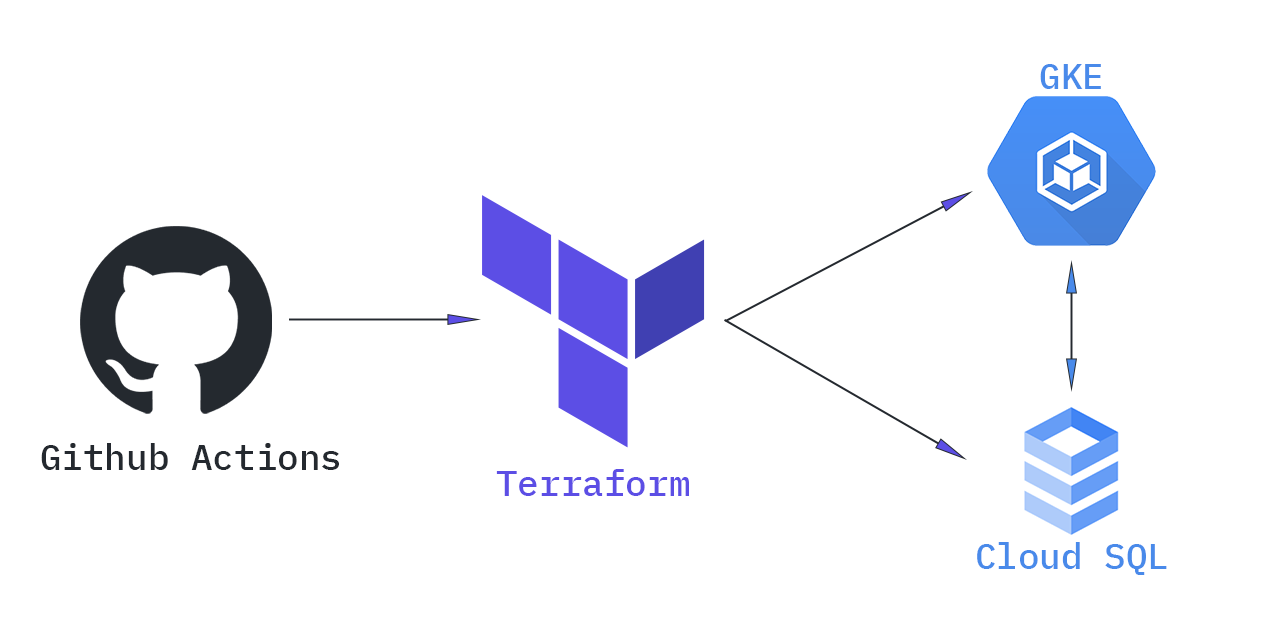
Create a Kubernetes cluster and a Cloud SQL instance in Google Cloud Platform.
Intro #
This article is an explanation for a Terraform sample code to create a GKE cluster and a Cloud SQL instance. The Pods in the GKE cluster have access to the Cloud SQL. It also configures a GitHub Actions pipeline to automate the changes.
The Source Code is available on GitHub.
Preparations #
Repo structure #
The environments/...
directories contain the environment files while the modules directory contains the reusable Terraform modules that are
used in the environments.
Dev #
The environments/dev
directory contains the resources for a dev environment.
Including the following modules:
- A dev Kubernetes cluster
- A Cloud SQL
- Service Accounts
- and more…
Modules #
k8s_cluster- Create the GKE cluster (it’s configured to use one node pool, and it configures a weekly backup).cloud_sql- Create a Google Cloud SQL PostgreSQL instance with the required network dependencies, an endpoint, and databases and users.
Pipelines #
The plan here is to create a pipeline
that runs on Pull Request to the main branch. It is triggered if there are any changes in the environments/dev or in
the modules directories. It initializes Terraform and runs terraform plan to check for any errors. A GitHub comment
is posted with the output of the plan to the Pull Request.
When the Pull Request is merged, the pipeline will run terraform apply to apply the changes to GCP.
Manual usage #
The tutorial repository utilises .envrc files to set the environment variables. You can use the direnv tool to automatically read
the .envrc file.
Terraform version is managed by tfenv.
Example usage:
$ cd environments/dev
$ direnv allow
$ tfenv install
$ terraform init
$ terraform plan
$ terraform apply